描述
给定一个二叉树,返回该二叉树层序遍历的结果,(从左到右,一层一层地遍历)
题解
- 首先判断二叉树是否为空,空树没有遍历结果
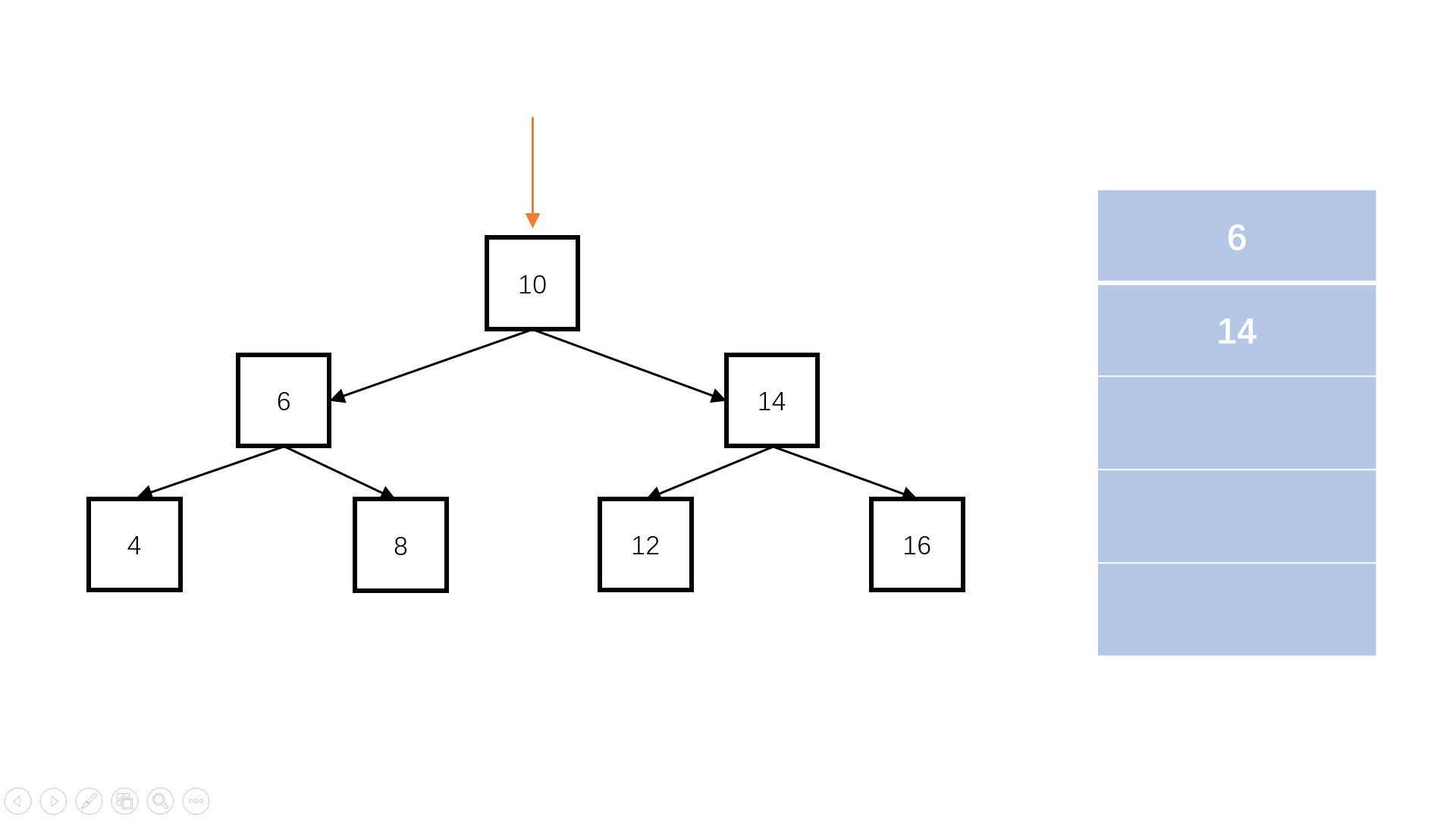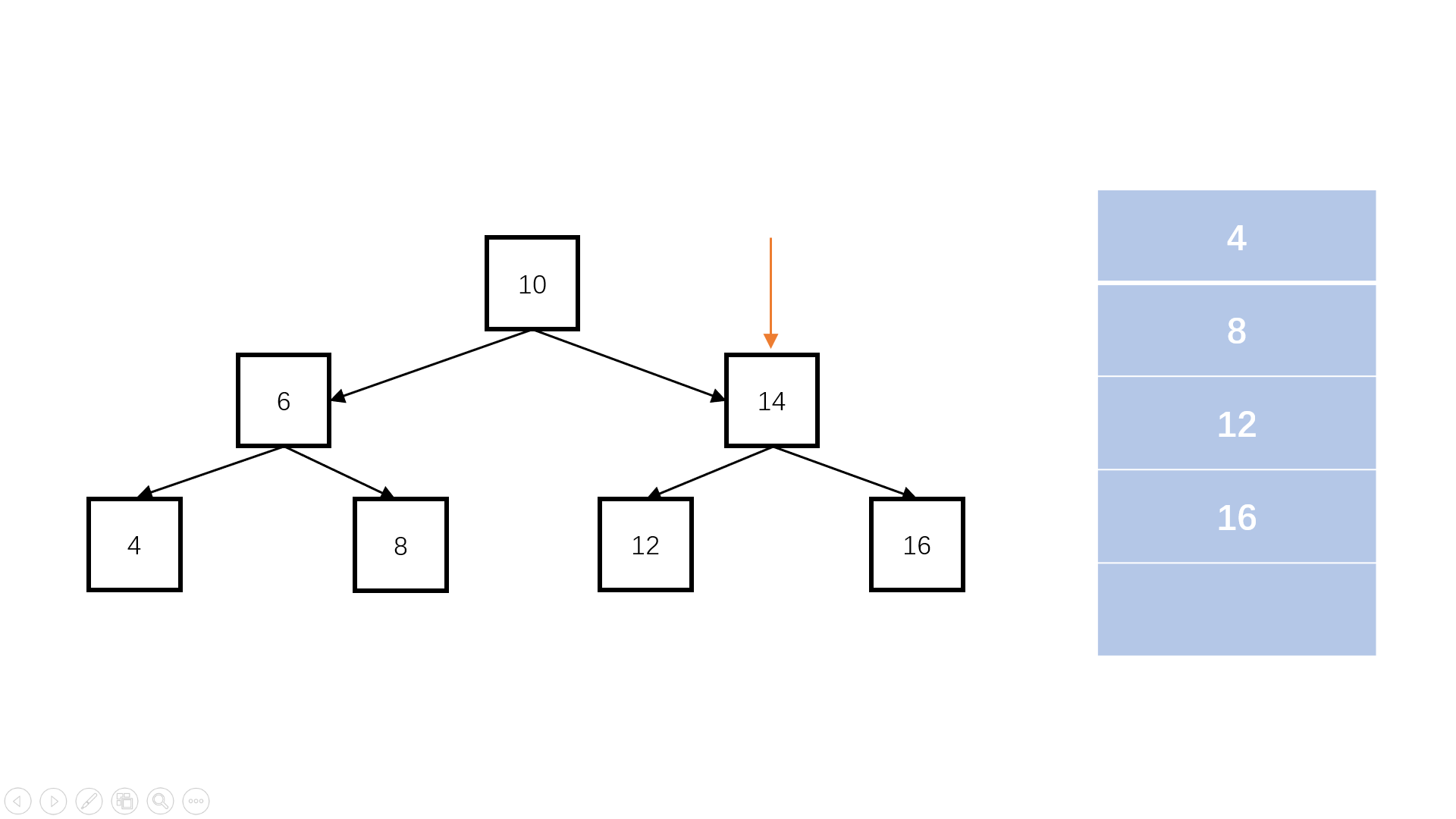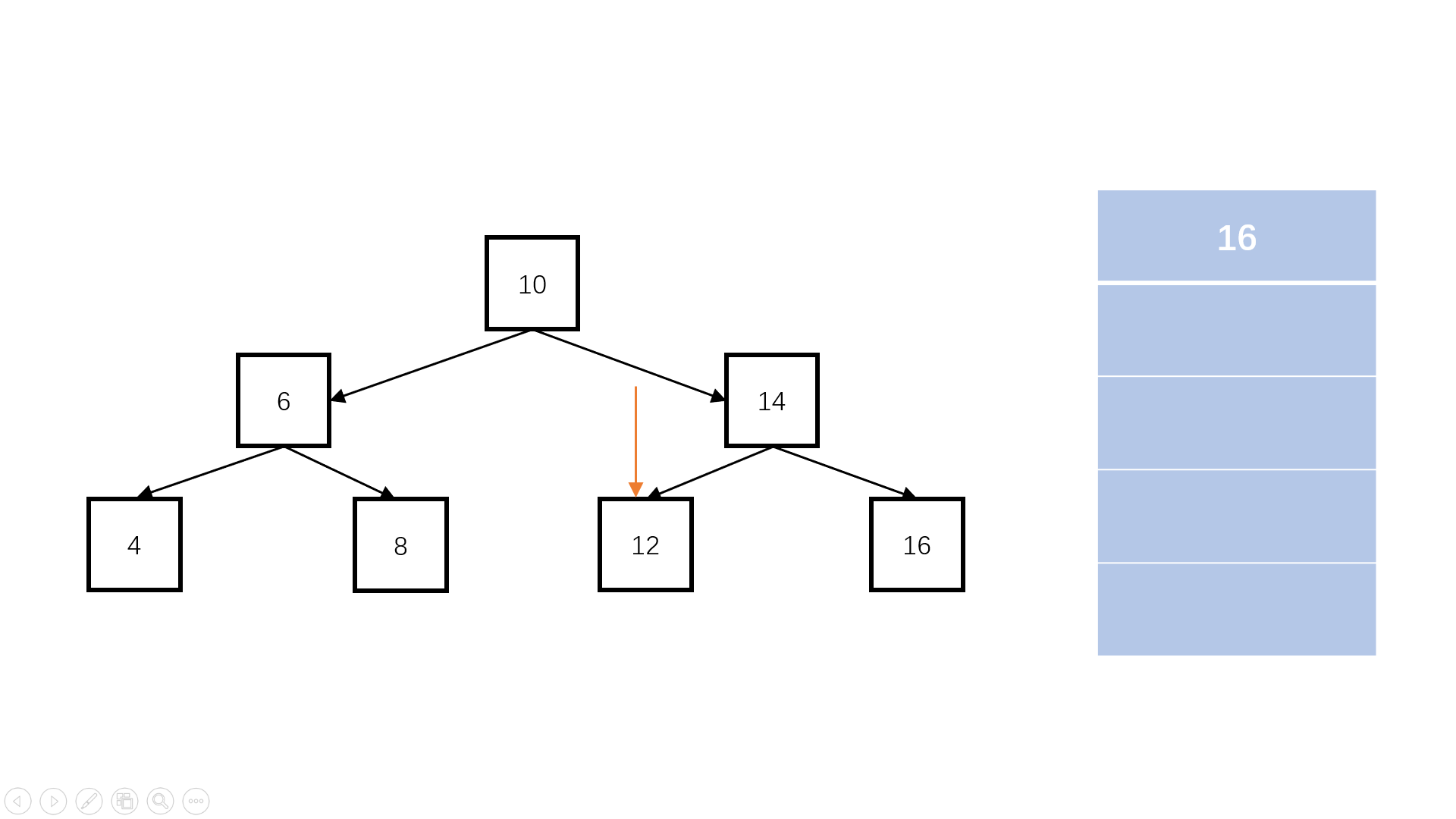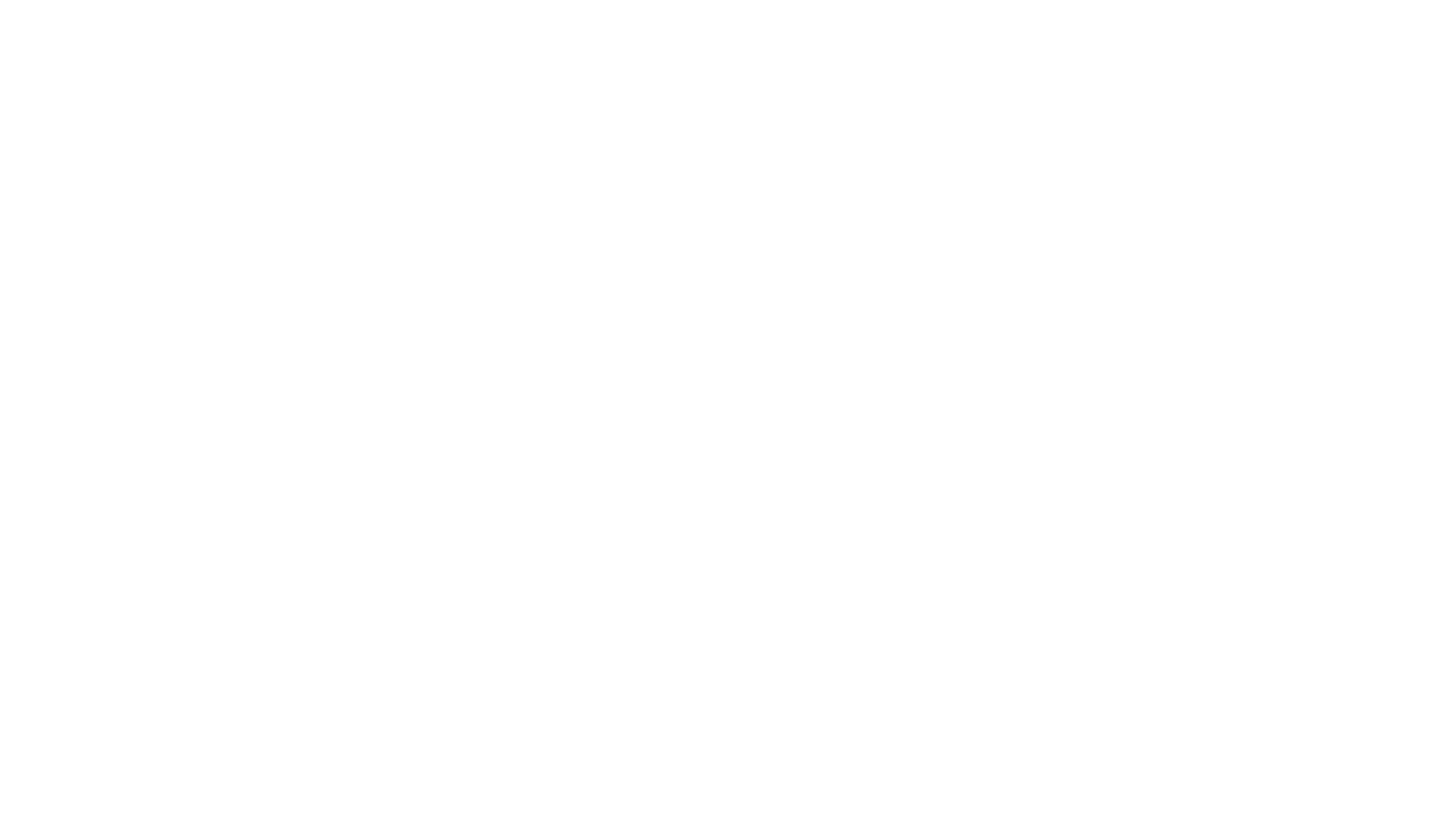
- 建立辅助队列,根节点首先进入队列。不管层次怎么访问,根节点一定是第一个,那它肯定排在队伍的最前面
- 每次进入一层,统计队列中元素的个数。因为每当访问完一层,下一层作为这一层的子节点,一定都加入队列,而再下一层还没有加入,因此此时队列中的元素个数就是这一层的元素个数
- 每次遍历这一层这么多的节点数,将其依次从队列中弹出,然后加入这一行的一维数组中,如果它们有子节点,依次加入队列排队等待访问
- 访问完这一层的元素后,将这个一维数组加入二维数组中,再访问下一层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package main
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func levelOrder( root *TreeNode ) [][]int {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
queues := []*TreeNode{}
queues = append(queues, root)
levels := [][]int{}
for len(queues) > 0 {
n := len(queues)
level := []int{}
for index :=0; index < n; index++ {
root := queues[0]
queues = queues[1:]
level = append(level, root.Val)
if root.Left != nil {
queues = append(queues, root.Left)
}
if root.Right != nil {
queues = append(queues, root.Right)
}
}
levels = append(levels, level)
}
return levels
}
|
